by Joche Ojeda | Mar 12, 2025 | dotnet, http, netcore, netframework, network, WebServers
Last week, I was diving into Uno Platform to understand its UI paradigms. What particularly caught my attention is Uno’s ability to render a webapp using WebAssembly (WASM). Having worked with WASM apps before, I’m all too familiar with the challenges of connecting to data sources and handling persistence within these applications.
My Previous WASM Struggles
About a year ago, I faced a significant challenge: connecting a desktop WebAssembly app to an old WCF webservice. Despite having the CORS settings correctly configured (or so I thought), I simply couldn’t establish a connection from the WASM app to the server. I spent days troubleshooting both the WCF service and another ASMX service, but both attempts failed. Eventually, I had to resort to webserver proxies to achieve my goal.
This experience left me somewhat traumatized by the mere mention of “connecting WASM with an API.” However, the time came to face this challenge again during my weekend experiments.
A Pleasant Surprise with Uno Platform
This weekend, I wanted to connect a XAF REST API to an Uno Platform client. To my surprise, it turned out to be incredibly straightforward. I successfully performed this procedure twice: once with a XAF REST API and once with the API included in the Uno app template. The ease of this integration was a refreshing change from my previous struggles.
Understanding CORS and Why It Matters for WASM Apps
To understand why my previous attempts failed and my recent ones succeeded, it’s important to grasp what CORS is and why it’s crucial for WebAssembly applications.
What is CORS?
CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing) is a security feature implemented by web browsers that restricts web pages from making requests to a domain different from the one that served the original web page. It’s an HTTP-header based mechanism that allows a server to indicate which origins (domains, schemes, or ports) other than its own are permitted to load resources.
The Same-Origin Policy
Browsers enforce a security restriction called the “same-origin policy” which prevents a website from one origin from requesting resources from another origin. An origin consists of:
- Protocol (HTTP, HTTPS)
- Domain name
- Port number
For example, if your website is hosted at https://myapp.com, it cannot make AJAX requests to https://myapi.com without the server explicitly allowing it through CORS.
Why CORS is Required for Blazor WebAssembly
Blazor WebAssembly (which uses similar principles to Uno Platform’s WASM implementation) is fundamentally different from Blazor Server in how it operates:
- Separate Deployment: Blazor WebAssembly apps are fully downloaded to the client’s browser and run entirely in the browser using WebAssembly. They’re typically hosted on a different server or domain than your API.
- Client-Side Execution: Since all code runs in the browser, when your Blazor WebAssembly app makes HTTP requests to your API, they’re treated as cross-origin requests if the API is hosted on a different domain, port, or protocol.
- Browser Security: Modern browsers block these cross-origin requests by default unless the server (your API) explicitly permits them via CORS headers.
Implementing CORS in Startup.cs
The solution to these CORS issues lies in properly configuring your server. In your Startup.cs file, you can configure CORS as follows:
public void ConfigureServices(IServiceCollection services) {
services.AddCors(options => {
options.AddPolicy("AllowBlazorApp",
builder => {
builder.WithOrigins("https://localhost:5000") // Replace with your Blazor app's URL
.AllowAnyHeader()
.AllowAnyMethod();
});
});
// Other service configurations...
}
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IWebHostEnvironment env) {
// Other middleware configurations...
app.UseCors("AllowBlazorApp");
// Other middleware configurations...
}
Conclusion
My journey with connecting WebAssembly applications to APIs has had its ups and downs. What once seemed like an insurmountable challenge has now become much more manageable, especially with platforms like Uno that simplify the process. Understanding CORS and implementing it correctly is crucial for successful WASM-to-API communication.
If you’re working with WebAssembly applications and facing similar challenges, I hope my experience helps you avoid some of the pitfalls I encountered along the way.
About Us
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/c/JocheOjedaXAFXAMARINC
Our sites
Let’s discuss your XAF
https://www.udemy.com/course/microsoft-ai-extensions/
Our free A.I courses on Udemy

by Joche Ojeda | Mar 11, 2025 | network
DNS and Virtual Hosting: A Personal Journey
In this article, I’m going to talk about a topic I’ve been working on lately because I’m creating a course on how to host ASP.NET Core applications on Linux. This is a trick that I learned a really long time ago.
I was talking with one of my students, Lance, who asked me when I learned all this hosting and server stuff. It’s actually a nice story.
My Early Server Adventures
When I was around 16 years old, I got a book on networking and figured out how to find free public IPs on my Internet provider’s network. A few years later, when I was 19, I got a book on Windows 2000 Server and managed to get a copy of that Windows version.
I had a great combination of resources:
- Public IPs that I was “borrowing” from my Internet provider
- A copy of Windows Server
- An extra machine (at that time, we only had one computer at home, unlike now where I have about 5 computers)
I formatted the extra computer using Windows Server 2000 and set up DNS using a program called Simple DNS. I also set up the IIS web server. Finally, for the first time in my life, I could host a domain from a computer at home.
In El Salvador, .sv domains were free at that time—you just needed to fill out a form and you could get them for free for many years. Now they’re quite expensive, around $50, compared to normal domains.
The Magic of Virtual Hosting
What I learned was that you can host multiple websites or web applications sharing the same IP without having to change ports by using a hostname or domain name instead.
Here’s how DNS works: When you have an internet connection, it has several parts—the IP address, the public mask, the gateway, and the DNS servers. The DNS servers essentially house a simple file where they have translations: this domain (like HotCoder.com) translates to this IP address. They make IP addresses human-readable.
Once requests go to the server side, the server checks which domain name is being requested and then picks from all the websites being hosted on that server and responds accordingly.
Creating DNS records was tricky the first time. I spent a lot of time reading about it. The internet wasn’t like it is now—we didn’t have AI to help us. I had to figure it out with books, and growing up in El Salvador, we didn’t always have the newest or most accurate books available.
The Hosts File: A Local DNS
In the most basic setup, you need a record which says “this domain goes to this IP,” and then maybe a CNAME record that does something similar. That’s what DNS servers do—they maintain these translation tables.
Each computer also has its own translation table, which is a text file. In Windows, it’s called the “hosts” file. If you’ve used computers for development, you probably know that there’s an IP address reserved for localhost: 127.0.0.1. When you type “localhost” in the browser, it translates to that IP address.
This translation doesn’t require an external network request. Instead, your computer checks the hosts file, where you can set up the same domain-to-IP translations locally. This is how you can test domains without actually buying them. You can say “google.com will be forwarded to this IP address” which can be on your own computer.
A Real-World Application
I used this principle just this morning. I have an old MSI computer from 2018—still a solid machine with an i7 processor and 64GB of RAM. I reformatted it last week and set up the Hyper-V server. Inside Hyper-V, I set up an Ubuntu machine to emulate hosting, and installed a virtual hosting manager called Webmin.
I know I could do everything via command line, but why write a lot of text when you can use a user interface?
Recently, we’ve been having problems with our servers. My business partner Javier (who’s like a brother to me) mentioned that we have many test servers without clear documentation of what’s inside each one. We decided to format some of them to make them clean test servers again.
One of our servers that was failing happens to host my blog—the very one you’re reading right now! Yesterday, Javier messaged me early in the morning (7 AM for me in Europe, around 9 PM for him in America) to tell me my blog was down. There seemed to be a problem with the server that I couldn’t immediately identify.
We decided to move to a bigger server. I created a backup of the virtual server (something I’ll discuss in a different post) and moved it to the Hyper-V virtual machine on my MSI computer. I didn’t want to redirect my real IP address and DNS servers to my home computer—that would be messy and prevent access to my blog temporarily.
Instead, I modified the hosts file on my computer to point to the private internal IP of that virtual server. This allowed me to test everything locally before making any public DNS changes.
Understanding DNS: A Practical Example
Let me explain how DNS actually works with a simple example using the domain jocheojeda.com and an IP address of 203.0.113.42.
How DNS Resolution Works with ISP DNS Servers
When you type jocheojeda.com in your browser, here’s what happens:
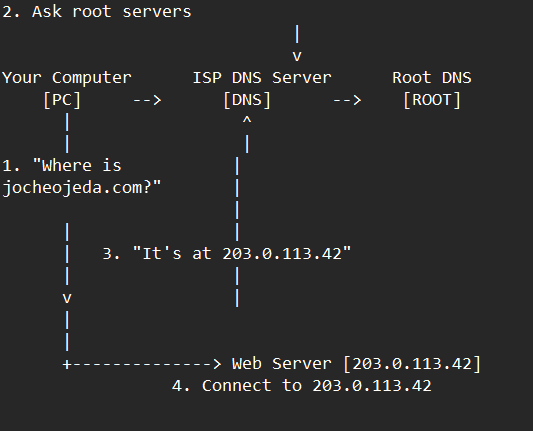
- Your browser asks your operating system to resolve
jocheojeda.com
- Your OS checks its local DNS cache, doesn’t find it, and then asks your ISP’s DNS server
- If the ISP’s DNS server doesn’t know, it asks the root DNS servers, which direct it to the appropriate Top-Level Domain (TLD) servers for
.com
- The TLD servers direct the ISP DNS to the authoritative DNS servers for
jocheojeda.com
- The authoritative DNS server responds with the A record:
jocheojeda.com -> 203.0.113.42
- Your ISP DNS server caches this information and passes it back to your computer
- Your browser can now connect directly to the web server at
203.0.113.42
DNS Records Explained
A Record (Address Record)
An A record maps a domain name directly to an IPv4 address:
jocheojeda.com. IN A 203.0.113.42
This tells DNS servers that when someone asks for jocheojeda.com, they should be directed to the server at 203.0.113.42.
CNAME Record (Canonical Name)
A CNAME record maps one domain name to another domain name:
www.jocheojeda.com. IN CNAME jocheojeda.com.
blog.jocheojeda.com. IN CNAME jocheojeda.com.
This means that www.jocheojeda.com and blog.jocheojeda.com are aliases for jocheojeda.com. When someone visits either of these subdomains, DNS will first resolve them to jocheojeda.com, and then resolve that to 203.0.113.42.
Using the Windows Hosts File
Now, let’s see what happens when you use the hosts file instead:
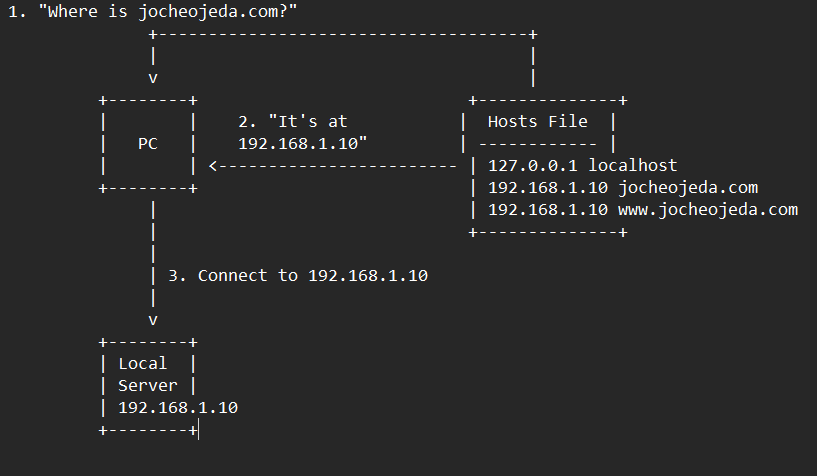
When using the hosts file:
- Your browser asks your operating system to resolve
jocheojeda.com
- Your OS checks the hosts file first, before any external DNS servers
- It finds an entry:
192.168.1.10 jocheojeda.com
- The OS immediately returns the IP
192.168.1.10 to your browser
- Your browser connects to
192.168.1.10 instead of the actual public IP
- The external DNS servers are never consulted
The Windows hosts file is located at C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts. A typical entry might look like:
# For local development
192.168.1.10 jocheojeda.com
192.168.1.10 www.jocheojeda.com
192.168.1.10 api.jocheojeda.com
This is incredibly useful for:
- Testing websites locally before going live
- Testing different server configurations without changing public DNS
- Redirecting domains during development or troubleshooting
- Blocking certain websites by pointing them to 127.0.0.1
Why This Matters for Development
By modifying your hosts file, you can work on multiple websites locally, all running on the same machine but accessible via different domain names. This perfectly mimics how virtual hosting works on real servers, but without needing to change any public DNS records.
This technique saved me when my blog server was failing. I could test everything locally using my actual domain name in the browser, making sure everything was working correctly before changing any public DNS settings.
Conclusion
Understanding DNS and how to manipulate it locally via the hosts file is a powerful skill for any developer or system administrator. It allows you to test complex multi-domain setups without affecting your live environment, and can be a lifesaver when troubleshooting server issues.
In future posts, I’ll dive deeper into server virtualization and how to efficiently manage multiple web applications on a single server.
About Us
YouTube
https://www.youtube.com/c/JocheOjedaXAFXAMARINC
Our sites
Let’s discuss your XAF
https://www.udemy.com/course/microsoft-ai-extensions/
Our free A.I courses on Udemy

by Joche Ojeda | Aug 15, 2024 | network, VPN
In the digital age, protecting one’s online privacy and circumventing internet censorship have become paramount concerns. Two prominent technologies addressing these concerns are Shadow Sockets and Virtual Private Networks (VPNs). While both offer ways to secure internet traffic, they differ significantly in their approach, application, and effectiveness.
What are Shadow Sockets?
Shadow Sockets (Shadowsocks) is an open-source encrypted proxy project, initially developed by a Chinese programmer known as “clowwindy” in 2012. It was created to bypass the Great Firewall of China, which imposes stringent restrictions on internet access. Unlike traditional VPNs, Shadowsocks focuses on bypassing censorship while maintaining a lightweight and high-performance connection.
History of Shadow Sockets
The creation of Shadowsocks was driven by the increasing internet censorship in China. Clowwindy designed Shadowsocks to be a secure and efficient method for users to access the uncensored internet. Over the years, the project has evolved, with numerous contributors enhancing its features and performance. In 2015, clowwindy announced that they had been contacted by Chinese authorities and would no longer be involved in the project. Despite this, the open-source nature of Shadowsocks allowed the community to continue its development, leading to various implementations and forks.
How Shadow Sockets Work
Shadowsocks operates by creating an encrypted tunnel between the user’s device and a proxy server located outside the censored area. This proxy server forwards the user’s internet traffic to its intended destination. Shadowsocks utilizes the SOCKS5 protocol, which ensures that the data passing through is secure and difficult to detect by censorship mechanisms.
Comparison Between Shadow Sockets and Traditional VPNs
Both Shadow Sockets and VPNs aim to secure internet traffic and provide access to restricted content. However, they differ in several key aspects:
1. Technology and Protocols
- VPNs: Traditional VPNs create a secure and encrypted tunnel between the user’s device and a VPN server using protocols like OpenVPN, L2TP/IPsec, or IKEv2. This tunnel encrypts all internet traffic, ensuring that data is secure from eavesdropping and interception.
- Shadowsocks: Shadowsocks uses the SOCKS5 proxy protocol. While it also creates an encrypted tunnel, it focuses on being less detectable by censorship mechanisms. Shadowsocks is designed to resemble regular HTTPS traffic, making it harder to block.
2. Performance
- VPNs: VPNs can sometimes slow down internet connections due to the overhead of encryption and the distance to the VPN server. The performance can vary based on the protocol used and the server’s location.
- Shadowsocks: Shadowsocks is typically faster and more lightweight compared to VPNs. Its design minimizes overhead, resulting in better performance and lower latency, especially useful in high-censorship environments.
3. Censorship Circumvention
- VPNs: While VPNs are effective at bypassing censorship, they can be blocked by advanced firewalls that detect VPN traffic. Countries with strict internet controls, like China and Iran, actively block known VPN servers and protocols.
- Shadowsocks: Shadowsocks excels in bypassing censorship due to its ability to mimic regular HTTPS traffic. This makes it more resilient against detection and blocking by sophisticated firewalls.
4. Use Cases
- VPNs: VPNs are widely used for general privacy protection, secure remote access to networks, and accessing geo-restricted content. They are favored for their ease of use and comprehensive encryption.
- Shadowsocks: Shadowsocks is preferred in environments with heavy censorship, where traditional VPNs are likely to be blocked. It’s often used by users in countries with stringent internet restrictions to access free and open internet.
5. Setup and Configuration
- VPNs: Setting up a VPN typically involves installing a client application and connecting to a server. Many VPN providers offer user-friendly apps for various devices.
- Shadowsocks: Shadowsocks setup can be more complex, often requiring manual configuration of the proxy settings. However, several third-party clients have simplified this process for end-users.
Conclusion
Both Shadow Sockets and traditional VPNs play crucial roles in securing internet traffic and bypassing censorship. However, their differences in technology, performance, and use cases make each suitable for specific scenarios. Shadowsocks, with its ability to evade detection and provide high performance, is particularly valuable in high-censorship environments. On the other hand, VPNs offer comprehensive security and ease of use, making them ideal for general privacy protection and accessing geo-restricted content. Understanding these differences can help users choose the right tool for their specific needs.
by Joche Ojeda | Apr 18, 2024 | network, Uncategorized
In today’s digital age, ensuring the security of our online activities and expanding the capabilities of our home networks are more important than ever. Two powerful tools that can help you achieve these goals are OpenVPN and DD-WRT. Here’s a straightforward guide to understanding what these technologies are and how they can be beneficial.
What is OpenVPN?
OpenVPN is a software application that allows you to create a secure connection over the internet between your computer and a server. Think of it as a protective tunnel for your internet traffic, shielding your data from prying eyes. This is particularly useful if you often use public Wi-Fi networks, which can be less secure and more vulnerable to hacking. By using OpenVPN, you can ensure that your sensitive information, such as passwords and personal details, are encrypted and safe from cyber threats.
Key Benefits of OpenVPN:
- Security: Encrypts your internet connection to provide enhanced security.
- Privacy: Masks your IP address, which helps keep your online activities private.
- Accessibility: Allows you to access websites and services that may be restricted in your area.
What is DD-WRT?
DD-WRT is a type of firmware that can replace the default firmware on your wireless router. Firmware is essentially the operating system that runs on your router, managing everything from network traffic to security features. Many factory-installed firmwares provide only basic functionalities. DD-WRT, on the other hand, is an open-source alternative that boosts your router’s capabilities significantly.
Key Benefits of DD-WRT:
- Enhanced Performance: Improves Wi-Fi signal strength and extends the range of your network.
- Advanced Features: Offers features like bandwidth monitoring, access controls, and the ability to set up a virtual private network (VPN).
- Customization: Allows more control over your network’s behavior and settings.
Why Combine OpenVPN with DD-WRT?
Using OpenVPN in conjunction with DD-WRT can transform your router into a powerful gateway that secures your entire home’s internet traffic. By installing OpenVPN on a DD-WRT router, you can ensure that all data passing through your router is encrypted, which adds an extra layer of security to every device connected to your network.
How Can You Get Started?
Setting up OpenVPN and DD-WRT might sound daunting, but there are plenty of resources and guides available to help you. Many communities and forums are dedicated to DD-WRT and OpenVPN, where you can find detailed instructions and get advice from experienced users. Additionally, considering a professional setup might be a good idea if you’re not comfortable undertaking the installation yourself.
Troubleshooting Common OpenVPN Issues on DD-WRT Routers
DD-WRT routers are popular for their robust features and flexibility compared to standard firmware shipped with wireless routers. However, setting up advanced features like an OpenVPN client can sometimes lead to errors if not configured correctly. Two common issues encountered during OpenVPN setups on DD-WRT routers are: unrecognized options in the configuration and errors related to Data Channel Offload (DCO). Here, we’ll walk through solutions to these problems, ensuring a smoother VPN experience.
Issue 1: Unrecognized Option “block-outside-dns“
Problem Description:
The error “Options error: Unrecognized option or missing or extra parameter(s) in [PUSH-OPTIONS]:3: block-outside-dns (2.6.10)” typically indicates that the OpenVPN client on DD-WRT does not recognize or support the `block-outside-dns` directive. This directive is commonly used on Windows clients to prevent DNS leaks but is not applicable or necessary for DD-WRT setups.
Solution Steps:
- Access Your VPN Server Configuration: Log into your OpenVPN server where your VPN configuration files are stored. This might be a PiVPN setup on a Raspberry Pi or any other Linux-based server running OpenVPN.
- Modify the Server Configuration:
- Restart the OpenVPN Service: Apply the changes by restarting the OpenVPN service with
sudo systemctl restart openvpn@server.
- Verify on DD-WRT: Reconnect the DD-WRT router to your VPN to ensure the error does not reappear.
Issue 2: Error Installing Key Material in DCO
Problem Description:
The error “Impossible to install key material in DCO: No such file or directory” refers to problems involving the Data Channel Offload feature, which is intended to enhance VPN performance by offloading certain processing tasks from the CPU.
Solution Steps:
- Check VPN Configuration Files: Ensure all necessary certificates and keys (CA certificate, client certificate, and client key) are correctly placed and accurately referenced in your DD-WRT’s VPN configuration.
- Disable DCO (If Unnecessary):
- DCO might not be supported adequately by all hardware or DD-WRT builds. To disable DCO, access the VPN configuration file on your router via the administration interface.
- Look for any DCO-related directives and disable them (comment out or remove). You can disable DCO by using the following line to the additional configuration section of your OpenVPN configuration
disable-dco
- Firmware Update: Confirm that your DD-WRT firmware is up to date, as updates may include fixes and enhancements for VPN functionalities.
- Check File Paths and Permissions: Use SSH to connect to your router and verify that all referenced files in your VPN configuration exist at the specified paths and have appropriate permissions.
- Consult Community Forums: If the issue persists, the DD-WRT community forums are a valuable resource for troubleshooting specific to your router model and firmware version.
Final Thoughts
Troubleshooting VPN issues on DD-WRT can be complex, but resolving these common errors can greatly enhance your network’s functionality and security. Ensuring that your VPN configuration is appropriate for your specific router and keeping your system up-to-date are critical steps in maintaining a secure and efficient network.
In conclusion, both OpenVPN and DD-WRT are excellent tools to enhance the security and functionality of your home network. Whether you’re looking to protect your personal information or simply want to boost your internet connection across your household, these technologies offer practical solutions that are worth considering. Embrace these tools to take control of your digital home environment and enjoy a safer, more efficient online experience.





